Grafana est une application open source multiplateforme permettant de représenter graphiquement des données provenant de différentes sources de données telles que InfluxDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL ou Prometheus. Aujourd’hui, je montre comment installer un service Grafana sur le diskstation Synology.
Étape 1 : Préparer Synology
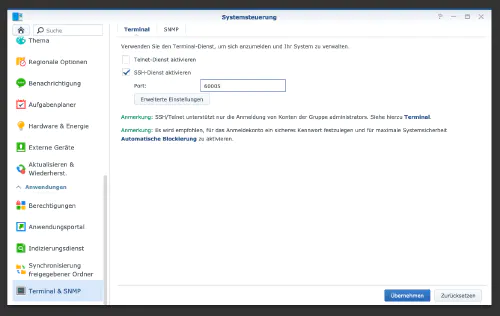
La première chose à faire est d’activer le login SSH sur le Diskstation. Pour cela, il faut aller dans le “Panneau de configuration” > “Terminal”.
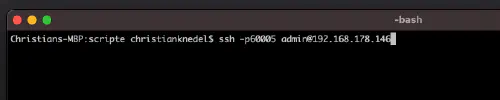
Ensuite, on peut se connecter via “SSH”, le port indiqué et le mot de passe de l’administrateur (les utilisateurs de Windows utilisent Putty ou WinSCP).
Je me connecte via Terminal, winSCP ou Putty et je laisse cette console ouverte pour plus tard.
Etape 2 : Créer un dossier Grafana
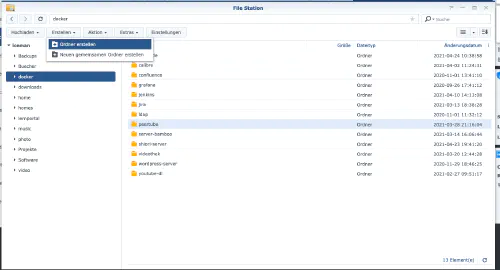
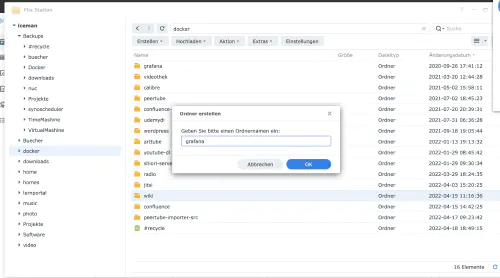
Je crée un nouveau répertoire appelé “grafana” dans le répertoire Docker.
Avec la commande “cd”, je recherche le répertoire Grafana :
$ cd /volume1/docker/grafana/
version: "2"
services:
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana
container_name: grafana_server_grafana
restart: always
ports:
- 3000:3000
networks:
- grafana
environment:
- GF_SERVER_CERT_FILE=/etc/ssl/server.crt
- GF_SERVER_CERT_KEY=/etc/ssl/server.key
- GF_SERVER_PROTOCOL=https
- GF_SERVER_HTTP_PORT=3000
volumes:
- ./grafana:/var/lib/grafana
- ./ssl:/etc/ssl
influxdb:
image: influxdb
container_name: grafana_server_influxdb
restart: always
ports:
- 8086:8086
networks:
- grafana
volumes:
- ./influxdb:/var/lib/influxdb
- ./ssl:/etc/ssl
environment:
- INFLUXDB_DB=telegraf
- INFLUXDB_USER=telegraf
- INFLUXDB_USER_PASSWORD=influxdb-password
- INFLUXDB_ADMIN_ENABLED=true
- INFLUXDB_ADMIN_USER=admin
- INFLUXDB_ADMIN_PASSWORD=influxdb-password
- INFLUXDB_HTTP_HTTPS_ENABLED=true
- INFLUXDB_HTTP_HTTPS_CERTIFICATE=/etc/ssl/server.crt
- INFLUXDB_HTTP_HTTPS_PRIVATE_KEY=/etc/ssl/server.key
- INFLUXDB_HTTP_AUTH_ENABLED=true
telegraf:
image: telegraf
container_name: grafana_server_telegraf
restart: always
environment:
HOST_PROC: /rootfs/proc
HOST_SYS: /rootfs/sys
HOST_ETC: /rootfs/etc
volumes:
- ./telegraf.conf:/etc/telegraf/telegraf.conf:ro
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro
- /sys:/rootfs/sys:ro
- /proc:/rootfs/proc:ro
- /etc:/rootfs/etc:ro
networks:
grafana:
Je crée encore deux sous-dossiers pour les données :
$ mkdir grafana
$ mkdir influxdb
$ chown -R 472:472 grafana
$ mkdir ssl
$ openssl genrsa -aes256 -passout pass:your-password -out ssl/server.pass.key 4096
$ openssl rsa -passin pass:your-password -in ssl/server.pass.key -out ssl/server.key
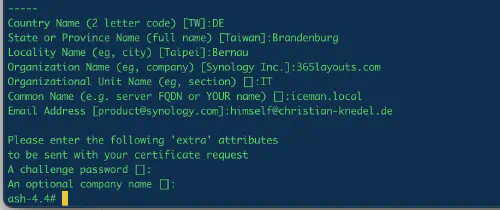
$ openssl req -new -key ssl/server.key -out ssl/server.csr
$ rm ssl/server.pass.key
$ openssl x509 -req -sha256 -days 365 -in ssl/server.csr -signkey ssl/server.key -out ssl/server.crt
En dernier lieu, je crée un fichier “telegraf.conf” avec ce contenu :
[global_tags]
[agent]
interval = "60s"
round_interval = true
metric_batch_size = 1000
metric_buffer_limit = 10000
collection_jitter = "0s"
flush_interval = "10s"
flush_jitter = "0s"
precision = ""
hostname = "Synology DS918"
omit_hostname = false
[[outputs.influxdb]]
urls = ["https://192.168.1.46:8086"] #synology ip
database = "telegraf"
timeout = "5s"
username = "telegraf"
password = "influxdb-password"
insecure_skip_verify = true
[[inputs.ping]]
interval = "5s"
urls = ["google.com", "amazon.com", "github.com"]
count = 4
ping_interval = 1.0
timeout = 2.0
[[inputs.cpu]]
percpu = true
totalcpu = true
collect_cpu_time = false
report_active = false
fielddrop = ["time_*"]
[[inputs.disk]]
ignore_fs = ["tmpfs", "devtmpfs", "devfs", "iso9660", "overlay", "aufs", "squashfs"]
[[inputs.disk]]
ignore_fs = ["tmpfs", "devtmpfs", "none", "iso9660", "overlay", "aufs", "squashfs"]
[[inputs.diskio]]
[[inputs.kernel]]
[[inputs.mem]]
[[inputs.swap]]
[[inputs.net]]
fieldpass = [ "bytes*" ]
[[inputs.netstat]]
[[inputs.processes]]
[[inputs.system]]
[[inputs.net]]
fieldpass = [ "bytes*" ]
[[inputs.docker]]
endpoint = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
gather_services = false
container_name_include = []
container_name_exclude = []
timeout = "5s"
docker_label_include = []
docker_label_exclude = []
perdevice = true
total = false
##
## Synology
##
[[inputs.snmp]]
# List of agents to poll
agents = [ "192.168.1.46" ] # required - enter the IP address of your Synology device
# Polling interval
interval = "60s"
# Timeout for each SNMP query.
timeout = "10s"
# Number of retries to attempt within timeout.
retries = 3
# SNMP version, UAP only supports v1
version = 2
# SNMP community string.
community = "public"
# The GETBULK max-repetitions parameter
max_repetitions = 30
# Measurement name
name = "snmp.SYNO"
# System name (hostname)
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
is_tag = true
name = "sysName"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysName.0"
# System vendor OID
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "sysObjectID"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysObjectID.0"
# System description
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "sysDescr"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysDescr.0"
# System contact
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "sysContact"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysContact.0"
# System location
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "sysLocation"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysLocation.0"
# System uptime
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "sysUpTime"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysUpTime.0"
# Inet interface
[[inputs.snmp.table]]
oid = "IF-MIB::ifTable"
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
is_tag = true
oid = "IF-MIB::ifDescr"
#Syno disk
[[inputs.snmp.table]]
oid = "SYNOLOGY-DISK-MIB::diskTable"
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
is_tag = true
oid = "SYNOLOGY-DISK-MIB::diskID"
#Syno raid
[[inputs.snmp.table]]
oid = "SYNOLOGY-RAID-MIB::raidTable"
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
is_tag = true
oid = "SYNOLOGY-RAID-MIB::raidName"
#Syno load
[[inputs.snmp.table]]
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::laTable"
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
is_tag = true
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::laNames"
# System memTotalSwap
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "memTotalSwap"
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::memTotalSwap.0"
# System memAvailSwap
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "memAvailSwap"
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::memAvailSwap.0"
# System memTotalReal
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "memTotalReal"
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::memTotalReal.0"
# System memAvailReal
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "memAvailReal"
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::memAvailReal.0"
# System memTotalFree
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "memTotalFree"
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::memTotalFree.0"
# System Status
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "systemStatus"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::systemStatus.0"
# System temperature
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "temperature"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::temperature.0"
# System powerStatus
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "powerStatus"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::powerStatus.0"
# System systemFanStatus
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "systemFanStatus"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::systemFanStatus.0"
# System cpuFanStatus
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "cpuFanStatus"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::cpuFanStatus.0"
# System modelName
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "modelName"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::modelName.0"
# System serialNumber
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "serialNumber"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::serialNumber.0"
# System version
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "version"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::version.0"
# System upgradeAvailable
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "upgradeAvailable"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::upgradeAvailable.0"
# System volume
[[inputs.snmp.table]]
oid = "HOST-RESOURCES-MIB::hrStorageTable"
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
is_tag = true
oid = "HOST-RESOURCES-MIB::hrStorageDescr"
# System ssCpuUser
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "ssCpuUser"
oid = ".1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.9.0"
# System ssCpuSystem
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "ssCpuSystem"
oid = ".1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.10.0"
# System ssCpuIdle
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "ssCpuIdle"
oid = ".1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.11.0"
# Service users CIFS
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersCIFS"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "1"
# Service users AFP
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersAFP"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "2"
# Service users NFS
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersNFS"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "3"
# Service users FTP
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersFTP"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "4"
# Service users SFTP
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersSFTP"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "5"
# Service users HTTP
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersHTTP"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "6"
# Service users TELNET
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersTELNET"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "7"
# Service users SSH
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersSSH"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "8"
# Service users OTHER
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersOTHER"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "9"
# UPS Status
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "upsStatus"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-UPS-MIB::upsInfoStatus"
# UPS Load
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "upsLoad"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-UPS-MIB::upsInfoLoadValue"
# UPS Battery Charge
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "upsCharge"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-UPS-MIB::upsBatteryChargeValue"
# UPS Battery Charge Warning
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "upsWarning"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-UPS-MIB::upsBatteryChargeWarning"
[[inputs.docker]]
endpoint = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
gather_services = false
container_name_include = []
container_name_exclude = []
timeout = "5s"
docker_label_include = []
docker_label_exclude = []
perdevice = true
total = false
Maintenant, démarre le serveur Grafana avec cet appel Compose :
$ sudo docker-compose -f grafana.yml up
Étape 3 : Configuration
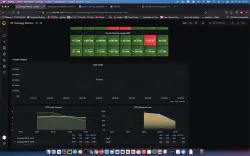
Je peux maintenant appeler le serveur, configurer la base de données, créer un tableau de bord et connecter d’autres données de mesure.